
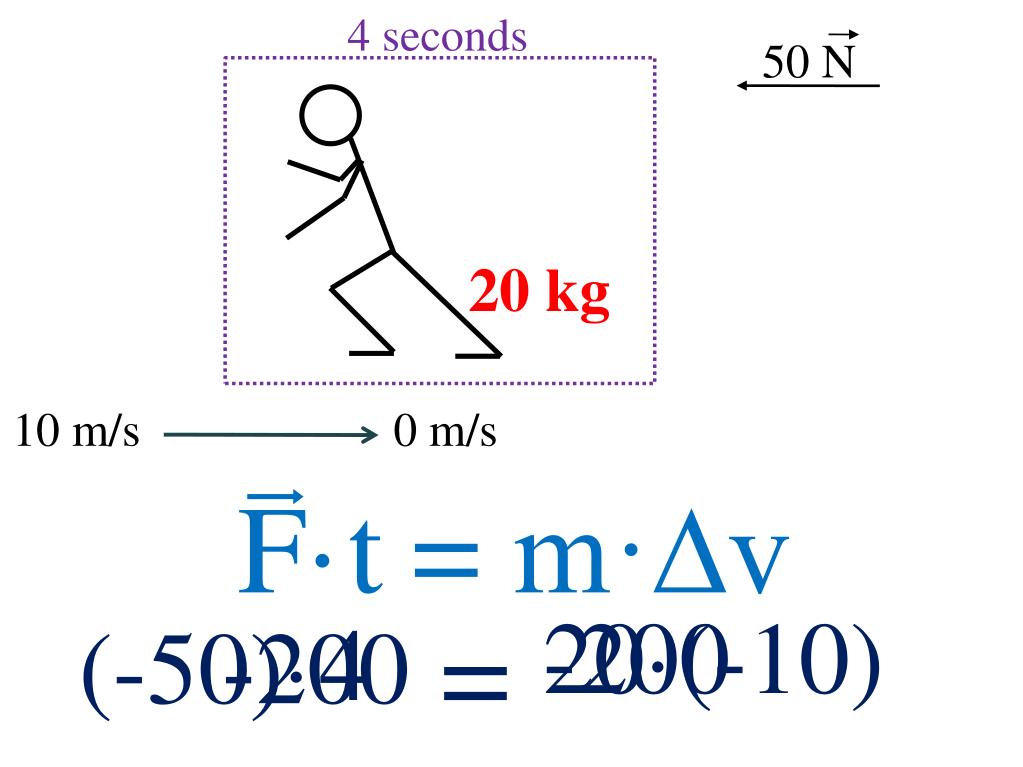
#An impulsive force of 100 n plus#
(continued) The particle’s initial momentum plus the sum of all the impulses applied from t1 to t2 is equal to the particle’s final momentum. ġ0 PRINCIPLE OF LINEAR IMPULSE AND MOMENTUM Graphically, it can be represented by the area under the force versus time curve. The impulse may be determined by direct integration. I acts in the same direction as F and has units of N It is a vector quantity measuring the effect of a force during its time interval of action. Linear impulse: The integral F dt is the linear impulse, denoted I. The linear momentum vector has units of (kg
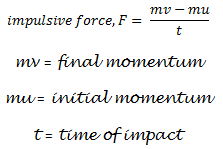
Linear momentum: The vector mv is called the linear momentum, denoted as L. It relates the particle’s final velocity (v2) and initial velocity (v1) and the forces acting on the particle as a function of time.ĩ PRINCIPLE OF LINEAR IMPULSE AND MOMENTUM (continued) The equation of motion can be written F = m a = m (dv/dt) Separating variables and integrating between the limits v = v1 at t = t1 and v = v2 at t = t2 results in mv2 – mv1 dv m F dt v2 v1 t2 t1 = ò å This equation represents the principle of linear impulse and momentum. (continued) The principle of linear impulse and momentum is obtained by integrating the equation of motion with respect to time. It can also be used to analyze the mechanics of impact (taken up in a later section).Ĩ PRINCIPLE OF LINEAR IMPULSE AND MOMENTUM This principle is useful for solving problems that involve force, velocity, and time. It can be applied to problems involving both linear and angular motion. The result is referred to as the principle of impulse and momentum. (Section 15.1) The next method we will consider for solving particle kinetics problems is obtained by integrating the equation of motion with respect to time. If we know the initial speed of the sledgehammer and the duration of impact, how can we determine the magnitude of the impulsive force delivered to the stake?ħ PRINCIPLE OF LINEAR IMPULSE AND MOMENTUM When a stake is struck by a sledgehammer, a large impulse force is delivered to the stake and drives it into the ground. Is the impulse a vector? Is the impulse pointing in the same direction as the force being applied? Given the situation of hitting a ball, how can we predict the resultant motion of the ball? The impulse is the average force exerted by the bat multiplied by the time the bat and ball are in contact.

How can we determine the magnitude of the linear impulse applied to the fender? Could you analyze a carpenter’s hammer striking a nail in the same fashion? Sure!Ī good example of impulse is the action of hitting a ball with a bat. To do so, the weight is gripped and jerked upwards, striking the stop ring. BĤ APPLICATIONS A dent in an trailer fender can be removed using an impulse tool, which delivers a force over a very short time interval. Which parameter is not involved in the linear impulse and momentum equation? A) Velocityě) Displacement C) Timeĝ) Force Answers: 1.

A) friction forceě) equation of motion C) kinetic energyĝ) potential energy 2. The linear impulse and momentum equation is obtained by integrating the _ with respect to time. In-Class Activities: Check Homework Reading Quiz Applications Linear Momentum and Impulse Principle of Linear Impulse and Momentum Concept Quiz Group Problem Solving Attention Quizģ READING QUIZ 1. Apply the principle of linear impulse and momentum. Today’s Objectives: Students will be able to: Calculate the linear momentum of a particle and linear impulse of a force. Presentation on theme: "PRINCIPLE OF LINEAR IMPULSE AND MOMENTUM"- Presentation transcript:Ģ PRINCIPLE OF LINEAR IMPULSE AND MOMENTUM


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
